NEW FUND OFFER(NFO) & INITIAL PUBLIC OFFER(IPO)
# What is a 'New Fund Offer(NFO)' ?
Definition: A new fund offer (NFO) is the first-time subscription offer for a new scheme launched by asset management companies (AMCs). A new fund offer is launched in the market to raise capital from the public in order to buy securities like shares, govt. bonds etc. from the market.
Description: NFO is similar to the initial public offer (IPO) with an attempt to raise capital from the market. NFOs are offered for a stipulated period. This means that the investors opting to invest in these schemes at the offer price (in most cases the offer price is fixed at Rs 10) can do so in this stipulated period only. After the NFO period, investors can take exposure to these funds only at the prevailing NAV.
# How do NFOs function?
The New Fund Offer (NFO) could be open-ended, allowing you to enter or withdraw at any moment. It might be closed-ended, requiring you to purchase the scheme’s units within a 15-day period. You are not permitted to redeem the investment before the stated maturity term.
During the limited period, investors can invest in the NFO units at a price of about Rs. 10 per unit. The fund’s subscription period ends, and the fund manager invests the corpus in equities in accordance with the scheme’s investing goals. The closed-ended mutual fund program is listed on the stock exchange, and the units may be bought and sold exactly like shares.
After the New Fund Offer (NFO) period has expired, investors can only purchase units in the mutual fund scheme at the current NAV. It is often greater than the NFO price. Investors might invest in non-financial offerings (NFOs) of debt schemes. Several investors, nevertheless, choose the new fund offerings of equity policies. Generally, NFO subscribers have been able to produce substantially higher profits post-listing.
# Types of Mutual Funds New Fund Offers (NFOs): There are 2 types of New Fund Offer (NFOs) Mutual Funds:-

# Things to keep in mind when investing in an NFO-
1. While NFO is an attractive opportunity to discover a new asset class or new investing strategies, and on the other, you do not have a proven long-term record of the scheme to study (Past performance may or may not be sustained in the future)
2. Since the NFO’s amount collection happens before the scheme goes live in the market, the fund manager may have some flexibility to hold on to the funds within the regulatory limits if the market is not favorable. Whereas, since the specific securities the fund will be investing in, may not be very clear, you may have to wait to be given details about the scheme’s investment portfolio.
Things to think about as an investor!
# Minimum Subscription Amount?
Typically, New Fund Offers stipulate a minimum subscription amount for investors. It may be as little as Rs. 500/- or as much as Rs. 5,000/-. As an investor, this might be your key criterion for narrowing down your potential investments. If the minimum membership price is more than you can afford, it is a good idea to reconsider your alternatives. In such circumstances, a Systematic Investment Plan (SIP) in an established high-performing scheme may be a more affordable and convenient option. CLICK HERE TO GO TO AMFI MUTUAL FUND NFO PAGE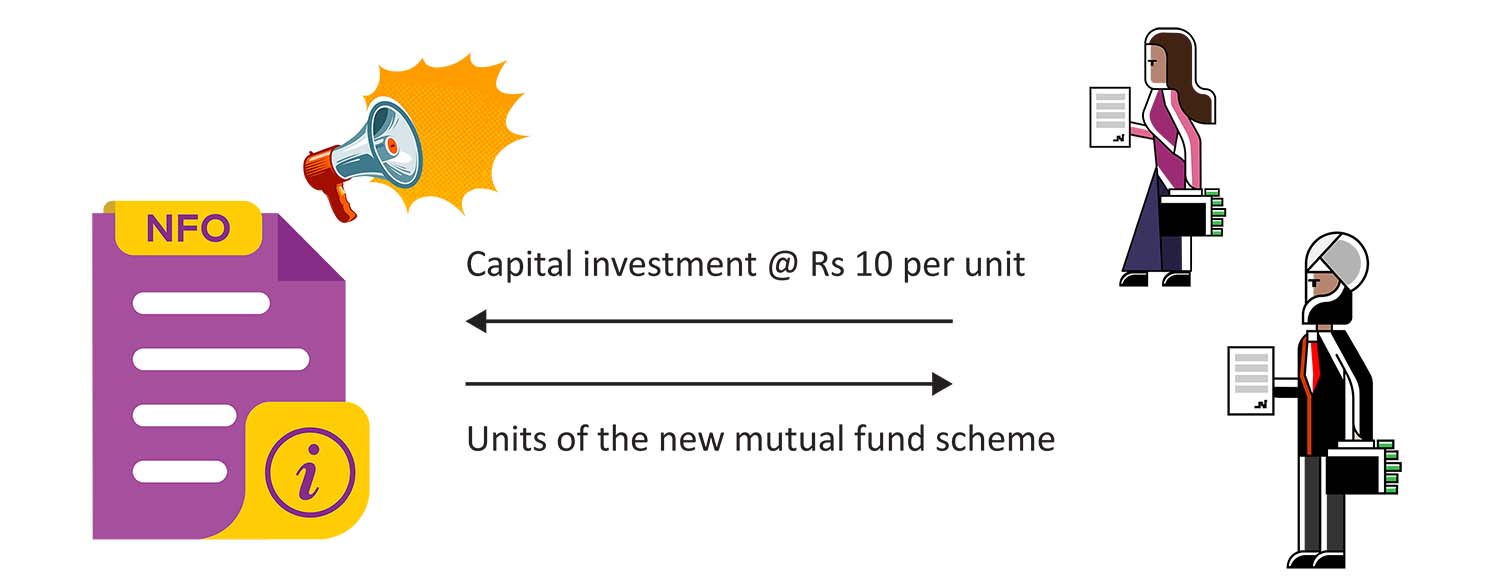 CLICK HERE TO GO TO NSE IPO DETAILS
CLICK HERE TO GO TO NSE IPO DETAILS
Initial Public Offer (IPO)
What Is an Initial Public Offering (IPO)?
An initial public offering (IPO) refers to the process of offering shares of a private corporation to the public in a new stock issuance for the first time. An IPO allows a company to raise equity capital from public investors.
The transition from a private to a public company can be an important time for private investors to fully realize gains from their investment as it typically includes a share premium for current private investors. Meanwhile, it also allows public investors to participate in the offering.
# KEY TAKEAWAYS:
- An initial public offering (IPO) refers to the process of offering shares of a private corporation to the public in a new stock issuance.

- Companies must meet requirements by exchanges and the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) to hold an IPO.
- IPOs provide companies with an opportunity to obtain capital by offering shares through the primary market.
- Companies hire investment banks to market, gauge demand set the IPO price and date, and more.
- An IPO can be seen as an exit strategy for the company’s founders and early investors, realizing the full profit from their private investment.
# How an Initial Public Offering (IPO) Works:
Before an IPO, a company is considered private. As a pre-IPO private company, the business has grown with a relatively small number of shareholders including early investors like the founders, family, and friends along with professional investors such as venture capitalists or angel investors.
An IPO is a big step for a company as it provides the company with access to raising a lot of money. This gives the company a greater ability to grow and expand. The increased transparency and share listing credibility can also be a factor in helping it obtain better terms when seeking borrowed funds as well.
When a company reaches a stage in its growth process where it believes it is mature enough for the rigors of SEC regulations along with the benefits and responsibilities to public shareholders, it will begin to advertise its interest in going public.
Typically, this stage of growth will occur when a company has reached a private valuation of approximately $1 billion, also known as unicorn status. However, private companies at various valuations with strong fundamentals and proven profitability potential can also qualify for an IPO, depending on the market competition and their ability to meet listing requirements.
IPO shares of a company are priced through underwriting due diligence. When a company goes public, the previously owned private share ownership converts to public ownership, and the existing private shareholders’ shares become worth the public trading price. Share underwriting can also include special provisions for private to public share ownership.
Generally, the transition from private to public is a key time for private investors to cash in and earn the returns they were expecting. Private shareholders may hold onto their shares in the public market or sell a portion or all of them for gains.
Meanwhile, the public market opens up a huge opportunity for millions of investors to buy shares in the company and contribute capital to a company’s shareholders' equity. The public consists of any individual or institutional investor who is interested in investing in the company.
Overall, the number of shares the company sells and the price for which shares sell are the generating factors for the company’s new shareholders' equity value. Shareholders' equity still represents shares owned by investors when it is both private and public, but with an IPO, the shareholders' equity increases significantly with cash from the primary issuance.